
National University of Kaohsiung / Prof. Yuan Ching
Pain Points Solved
Currently, massive amounts of industrial waste (such as waste tires and waste molding compounds from the optoelectronic industry) are difficult to reuse effectively, resulting in environmental pollution and resource waste. This technology utilizes innovative recycling and process designs to transform these low-value wastes into high-value-added Silicon Carbide (SiC) products, balancing both environmental protection and economic benefits.
Technology Introduction
This technology utilizes recovered carbon black from waste tires as a carbon source and waste molding compounds from the optoelectronic industry as a silicon source. By employing carbothermal reduction combined with integrated mechanical and thermal activation procedures, it successfully prepares silicon carbide nanomaterials with granular and whisker structures. This process effectively lowers the reaction temperature threshold, reduces energy consumption, and decreases carbon dioxide emissions by 7.4–12.5 kg for every kilogram of silicon carbide produced, significantly improving the carbon footprint of traditional processes.
Furthermore, the resulting silicon carbide material possesses excellent mechanical strength and photocatalytic properties: when added to tire rubber, it enhances cohesion and tear strength by over 10%; when applied to coatings and epoxy resins, it strengthens resistance to compression, shear, and abrasion; as a photocatalytic composite film, it can degrade over 92% of tetracycline pollutants within 240 minutes.
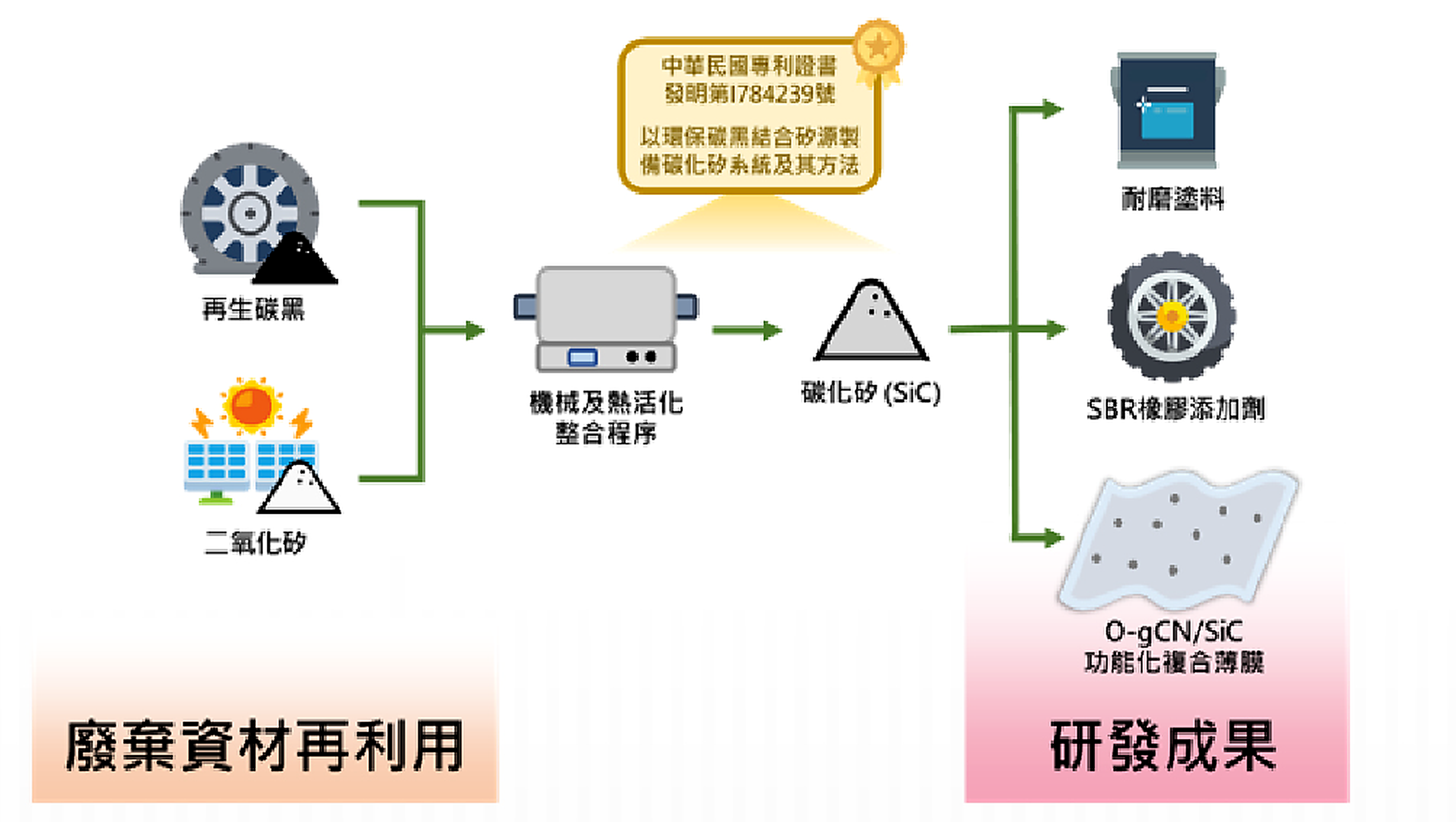
Figure 1. System and Method for Preparing Silicon Carbide by Combining Environmental Carbon Black with Silicon Source
Application Examples
Silicon Carbide Applications:
Functional Films:
Water Purification Systems: Can be applied in membrane filtration procedures within reclaimed water or sewage treatment systems to remove minute particles and organic substances.
Air Purification: Can serve as air filters; combined with photocatalysis, effectively removing organic substances from indoor air.
Self-Cleaning Products:
The film is hydrophobic, resisting water stains; the addition of photocatalysts prevents grime accumulation on the surface.
Related Links
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=otNuGbpGtTw
Patent Name and Number
None
Industry-Academia / Tech Transfer Partner
None
Honors and Awards
None
Technical Contact
Vivian Lee, Administrative Assistant
National University of Kaohsiung
Tel: +886 7-5916639
Email: vivianlee@nuk.edu.tw